Can allergies cause loss of taste? Yes, allergies can manifest in various ways, and one lesser-known symptom is the loss of taste. It can greatly affect one’s quality of life, as taste plays a crucial role in our enjoyment of food and beverages. Maybe Mama’s home cooking doesn’t hit like it used to. No fun! Let’s delve deeper into the relationship between allergies and the senses.

Table of Contents
Is the loss of taste a symptom of allergies?
Yes, the loss of taste can be a symptom of allergies. Inflammation plays a significant role in taste loss associated with allergies. When allergens enter the body, they trigger an immune response, causing the release of inflammatory mediators, such as histamine.
Histamine, in particular, can have a negative impact on the nasal passages, leading to swelling and congestion. The inflammation can then spread to the olfactory nerves, impairing their function and resulting in a diminished sense of taste.
How Allergies Affect Taste

Your loss of taste could be from your seasonal allergy symptoms, as our senses, particularly taste, and smell, are intricately connected. For example, if your allergies give you a runny or clogged nose, this can affect how well you can taste.
When we eat, the flavors we perceive are a combination of taste and smell sensations. Our taste buds detect basic tastes like sweet, sour, bitter, salty, and umami, while our sense of smell contributes significantly to the overall perception of flavor.
Therefore, any disruption in our sense of smell can have a significant impact on how we experience taste.
Loss of Taste and Smell with Allergies

Allergies can cause loss of taste and smell at the same time. Brainfacts.org explains that taste is closely tied to smell. To taste and smell our bodies need some food molecules to activate our neurons and send the information to our brains. These food molecules can become airborne when we are cooking or preparing foods and our nose picks up on these tiny food particles floating around in the air.
When we chew food, we break up what we are eating which allows our tongues to taste. Additionally, we are releasing some food particles that can also be detected by our noses.
If our noses are compromised due to allergy symptoms, this can definitely cause a loss of taste and smell, since taste and smell work together.
Medications That Cause Loss of Taste
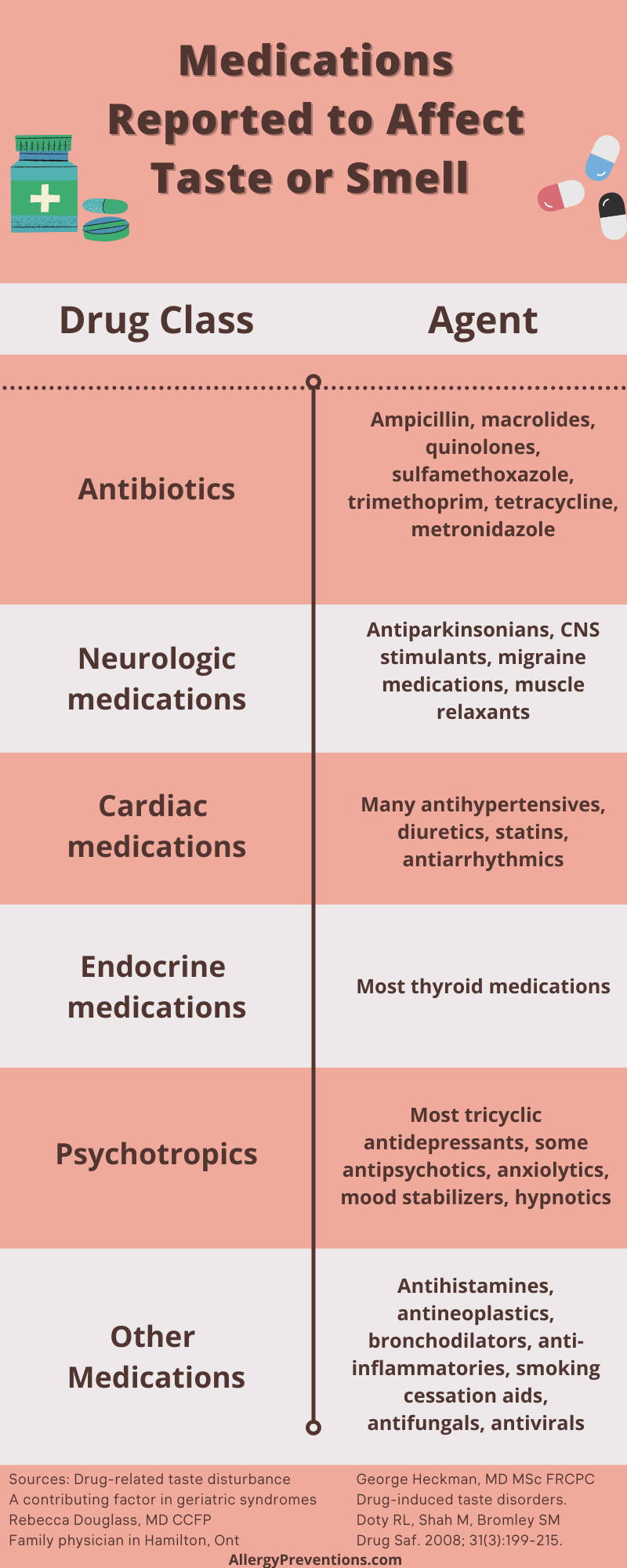
Certain medications can alter a person’s sense of taste, and how they perceive flavor. The most likely drugs to cause taste disturbances are:
- Antibiotics: Ampicillin, macrolides, quinolones, sulfamethoxazole, trimethoprim, tetracycline, metronidazole
- Cardiac medications: Many antihypertensives, diuretics, statins, antiarrhythmics
- Endocrine medications: Most thyroid medications
- Neurologic medications: Antiparkinsonians, CNS stimulants, migraine medications, muscle relaxants
- Other medications: Antihistamines, antineoplastics, bronchodilators, anti-inflammatories, smoking cessation aids, antifungals, antivirals
- Psychotropics: Most tricyclic antidepressants, some antipsychotics, anxiolytics, mood stabilizers, hypnotics
How Medications Affect Taste
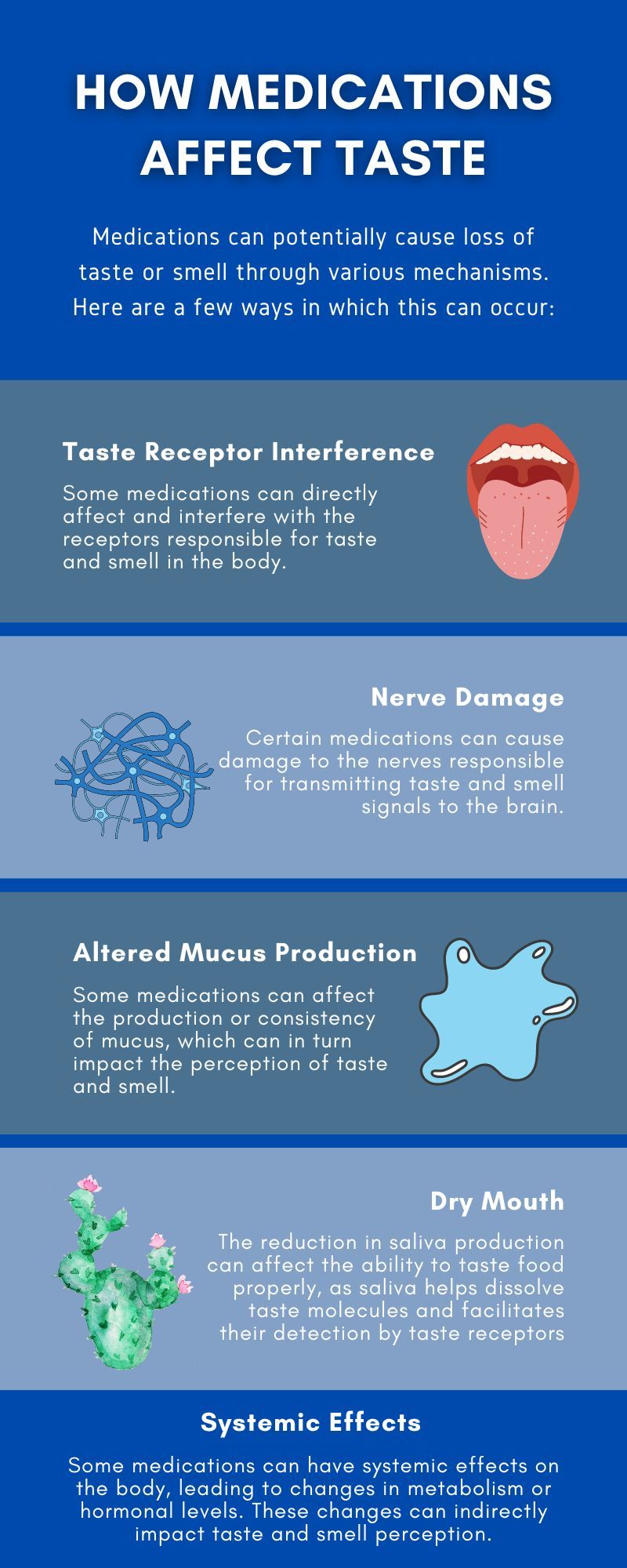
Medications can potentially cause loss of taste or smell through various mechanisms. Here are a few ways in which this can occur:
- Direct effect on taste or smell receptors: Some medications can directly affect the receptors responsible for taste and smell in the body. They may interfere with the normal functioning of these receptors, resulting in a diminished ability to taste or smell.
- Nerve damage: Certain medications, particularly those used in chemotherapy or for the treatment of neurological conditions, can cause damage to the nerves responsible for transmitting taste and smell signals to the brain. When these nerves are affected, it can lead to a loss of taste or smell.
- Altered mucus production: The ability to taste and smell is also influenced by the presence of mucus in the nasal passages and oral cavity. Some medications can affect the production or consistency of mucus, which can in turn impact the perception of taste and smell.
- Dry mouth: Certain medications can cause dry mouth as a side effect. The reduction in saliva production can affect the ability to taste food properly, as saliva helps dissolve taste molecules and facilitates their detection by taste receptors.
- Systemic effects: Some medications can have systemic effects on the body, leading to changes in metabolism or hormonal levels. These changes can indirectly impact taste and smell perception.
Loss of Taste from Medications Incidence Rates
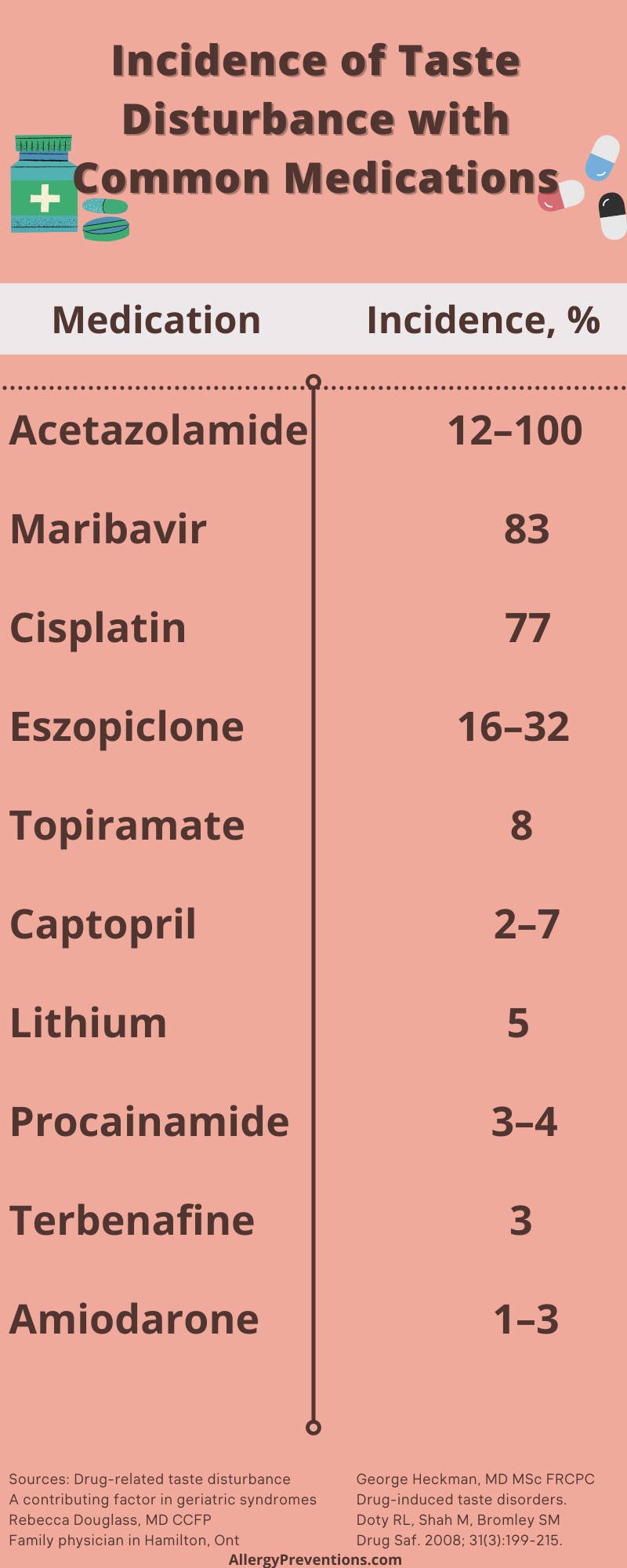
Medications have different incident rates for causing loss of taste. Here are the percentages of how often each medication causes a taste disturbance:
- Acetazolamide: 12-100%
- Maribavir: 83%
- Cisplatin: 77%
- Eszopiclone: 16-32%
- Topiramate: 8%
- Captopril: 2-7%
- Lithium: 5%
- Procainamide: 3-4%
- Terbenafine: 3%
- Amiodarone: 1-3%
It’s important to note that not all medications cause loss of taste or smell, and the likelihood and severity of these side effects can vary from person to person. If you are experiencing a loss of taste or smell while taking medication, it’s recommended to consult your healthcare provider for further evaluation and guidance.
Other Causes of Loss of Taste

There are other causes of loss of taste besides allergies. Here is a list of the common factors that can also contribute to losing the ability to taste:
- Aging
- Congestion and illness
- Dental problems
- Drinking and smoking
- Medications
- Nerve damage
- Vitamin deficiency
Aging

Ah, aging. It’s a part of life, folks. As we gracefully (or not so gracefully) age, our bodies go through some changes, and our taste buds are no exception. You might have noticed that your once-favorite flavors don’t seem as vibrant as they used to be. Well, blame it on the aging process! As we get older, our taste buds naturally become less sensitive, making it harder to fully experience the nuances of taste.
Congestion and Illness

First up, we have nasal congestion. When your nose is all stuffed up, it can affect your sense of taste. You see, the olfactory receptors in your nose play a crucial role in your ability to perceive flavors. So, when those receptors are blocked or impaired, your taste buds might not receive the full signal, resulting in a temporary loss of taste.

Next on the list is upper respiratory infections, such as the common cold or sinusitis. These pesky infections can throw your taste buds off balance, leaving you with a diminished ability to savor the flavors. But fear not, as this is usually a temporary setback that fades away once the infection clears up.
Dental Problems

You know, those pesky toothaches and gum issues that can make your taste buds go, “Wait, what? I can’t taste that!” When you’re dealing with oral health woes like cavities, gum disease, or even tooth loss, it can mess with your ability to fully experience those delicious flavors.
Drinking and Smoking

Last but not least, we have smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. These habits can take a toll on your taste buds over time. They can dull your senses, making it harder to fully appreciate the flavors of your favorite foods and beverages. So, if you’re a fan of these indulgences, it might be worth considering the impact they can have on your taste buds.
Medications

Certain medications can also play a part in bidding farewell to your taste buds’ abilities. Some antibiotics, antihistamines, and even chemotherapy drugs can interfere with your sense of taste. It’s like they’re playing a game of hide-and-seek with your taste buds, making the flavors harder to detect. If you suspect your medication might be the culprit, it’s always a good idea to check in with your healthcare provider for guidance.
Nerve Damage

Your taste buds rely on a network of nerves to transmit those taste signals to your brain, giving you that sweet sensation of yumminess. But sometimes, due to injuries, surgeries, or even certain medical conditions, these nerves can get a little out of whack. And when that happens, you might find yourself in a taste bud Twilight zone, where the flavors just don’t hit the mark like they used to.
Vitamin Deficiency

Now, here’s an unexpected twist: nutritional deficiencies. Yep, not getting enough of certain vitamins and minerals can affect your taste buds’ performance. For example, a lack of zinc or vitamin B12 can throw your taste buds into a bit of a frenzy. So, it’s important to maintain a balanced diet and ensure you’re getting all the essential nutrients your body needs.
It’s important to note that if you are experiencing a sudden or persistent loss of taste, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment. They can help identify the underlying cause and recommend the necessary steps to address the issue.
Allergy Treatment Options
Luckily there are some options when it comes to treating your allergies. I know allergies can be a real pain in the nose, but fear not because I’ve got some great solutions for you. So grab a tissue and let’s dive in!
Over-the-Counter Medications

When it comes to allergies, over-the-counter medications are often the first line of defense. Antihistamines like Claritin and Zyrtec can provide relief from sneezing, itching, and a runny nose. Just be sure to follow the recommended dosage and consult a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
Nasal Sprays

If you’re dealing with nasal congestion and inflammation, nasal sprays can work wonders. Products like Flonase and Nasacort can help reduce swelling in your nasal passages and relieve that annoying stuffy feeling. Pro tip: aim for your nostrils, not your eyes—trust me on this one!
Allergy Shots
For those of you with severe allergies, allergy shots might be the way to go. These injections, also known as immunotherapy, can help desensitize your immune system to specific allergens over time. It’s almost like a vaccine against allergies. I have received allergy shots for a few years and they help!
Eye Drops

Ah, the dreaded itchy, watery eyes. Don’t worry, there are eye drops available to save the day! Look for products that contain an antihistamine, which can provide quick relief from eye-related allergy symptoms. Plus, they’ll make you look less like you just watched “Marley & Me” for the hundredth time.
Avoidance and Environmental Control

The best way to deal with environmental or seasonal allergies is to avoid the triggers altogether. For example, if you’re allergic to pollen, try to stay indoors on high-pollen days or use air purifiers to filter the air.
Dust mite allergies? Wash your bedding regularly and consider using allergen-proof covers. And if you’re allergic to your neighbor’s cat, maybe ask them to put a tiny tuxedo on it. Hey, it’s worth a shot!
Remember, everyone’s allergies are unique, so what works for one person might not work for another. If you’re unsure about the best treatment option for you, it’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional or an allergist. They’ll be able to guide you in the right direction and help you find relief from those pesky allergies.
Did you know: Allergies might cause hearing loss?
