Understanding tree nut allergies, their symptoms, causes, and management strategies is crucial for individuals, families, and communities. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the various aspects of tree nut allergies, providing insights, tips, and expert advice for navigating life with this condition.

As an Amazon Affiliate, I may get a commission on qualifying purchases at no cost to you.
Table of Contents
Understanding Tree Nut Allergies

Tree nut allergies are a type of food allergy that refers to adverse immune reactions triggered by the consumption or exposure to nuts from trees. These allergies can range from mild to severe and may cause life-threatening reactions in some individuals.
Those affected must carefully read labels and inquire about ingredients, as even small traces of tree nuts can provoke a response. Avoiding products processed in facilities that handle tree nuts may also be necessary due to the risk of cross-contamination.
Tree Nuts That Trigger Allergies List

Many different types of tree nuts can cause allergic reactions. Here is a list of the top 10 tree nuts that may invoke allergies:
- Almonds
- Brazil Nuts
- Cashews
- Chestnuts
- Hazelnuts
- Macadamia Nuts
- Pecans
- Pine Nuts
- Pistachios
- Walnuts
How common are tree nut allergies?

Tree nut allergies are fairly common, with over 3.3 million people in the U.S. being allergic to tree nuts. While this may seem like a small percentage, it’s still significant considering the potential severity of allergic reactions.
To give you a comparison of just how common tree nut allergies are, peanut allergies affect 1.6 million people in the U.S. which is half of the 3.3 million tree nut allergy sufferers.
Why do I suddenly have a tree nut allergy?

Developing a sudden tree nut allergy can be perplexing and concerning in both children and adults. Allergies can develop at any stage of life, even if you’ve previously consumed the allergen without any adverse reactions.
The good news is that as time goes on your immune system changes, which can potentially lead to overcoming tree nut allergies. Of course, this is not something that happens with everyone, but there is a chance!
Tree Nut Allergy Causes and Risk Factors

Tree nut allergies develop when the immune system mistakenly identifies proteins in tree nuts as harmful invaders. The exact cause is unknown. Certain risk factors may increase the likelihood of developing a tree nut allergy, including a family history of allergies, having other food allergies, or having asthma or eczema.
- Cross-Reactivity: Some individuals with allergies to one type of tree nut may experience cross-reactivity with other tree nuts or even with certain fruits or vegetables due to similarities in protein structures.
- Early Exposure: Introducing tree nuts into a child’s diet too early or too late may increase the likelihood of developing an allergy.
- Environmental Factors: Environmental factors, such as pollution, climate changes, and exposure to certain chemicals, may contribute to the development of allergies by influencing the immune system’s response to allergens.
- Genetics: Family history plays a significant role in the development of allergies. If you have close relatives with allergies, particularly to tree nuts, you may have a higher risk of developing a similar allergy.
- Gut Health: Emerging research suggests a potential link between gut health and the development of allergies. Disruptions in the balance of gut bacteria or intestinal permeability may contribute to allergic sensitization.
- Other Allergies: Individuals with existing allergies, such as pollen or other food allergies, may be at higher risk of developing additional allergies, including tree nut allergies. This phenomenon is known as the allergic march or atopic march.
- Other Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as eczema or asthma, may increase the risk of developing allergies, including tree nut allergies.
It’s important to note that while these factors can contribute to the development of tree nut allergies, not everyone with these risk factors will develop an allergy, and individuals without these risk factors can still develop allergies.
If you suspect you have a tree nut allergy or are at risk, consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis, management, and guidance on allergen avoidance.
Tree Nut Allergy Symptoms

Tree nut allergy symptoms can vary in severity from mild to life-threatening. They typically occur shortly after consuming tree nuts or products containing tree nuts, but in some cases, they can also occur through contact or inhalation of tree nut particles. Common symptoms of a tree nut allergy include:
- Digestive Issues: Nausea, vomiting, stomach cramps, diarrhea, or other gastrointestinal symptoms.
- Oral Allergy Syndrome: Some individuals may experience itching or tingling in the mouth or throat after consuming certain tree nuts.
- Respiratory Symptoms: Runny or stuffy nose, sneezing, coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, or difficulty breathing.
- Skin Reactions: Itching, redness, swelling, or hives (urticaria) on the skin, particularly around the mouth or face, but can occur anywhere on the body.
It’s essential to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms of a tree nut allergy, especially if they are severe or if you have a history of anaphylaxis.
How long do tree nut allergy symptoms last?
The duration of tree nut allergy symptoms can vary depending on the severity of the reaction and how quickly treatment is administered. Mild symptoms, such as itching or mild skin reactions, may resolve on their own within a few hours after exposure to the allergen.
Diagnosing Tree Nut Allergies

Understanding how to accurately diagnose tree nut allergies is crucial for you to manage your health effectively. Several methods are used to diagnose tree nut allergies, each offering unique advantages and considerations. The most common diagnostic tests include skin prick tests, blood tests, and oral food challenges.
Skin Prick Tests
A skin prick test involves introducing a small amount of various tree nut proteins under the skin’s surface and observing the body’s reaction. A positive result, indicated by a raised bump or redness, suggests an allergy to that specific nut.
My Skin Prick Test Experience
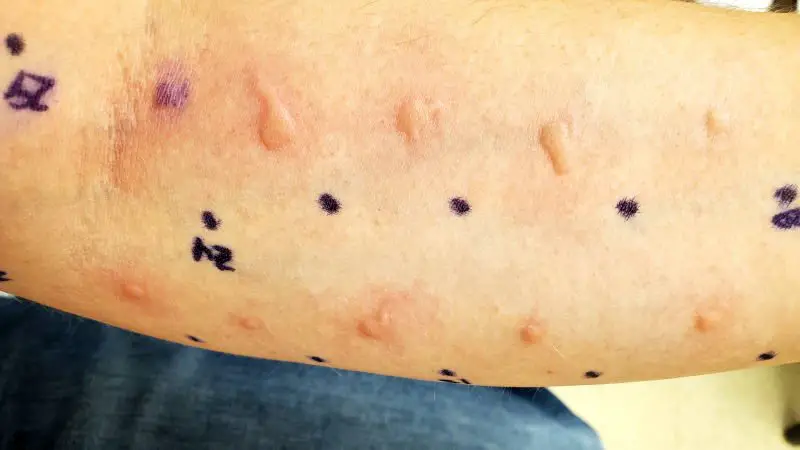
Based on my experience, undergoing a skin prick test proves worthwhile despite the discomfort it entails. When the allergist introduces small amounts of allergens beneath the skin, itching can become quite bothersome.
Nevertheless, the certainty of identifying one’s allergens outweighs the temporary discomfort. Understanding what substances to avoid is invaluable, even if it means enduring swollen and itchy skin during the test.
Blood Tests
Blood tests measure the presence of specific antibodies in the bloodstream that are indicative of an allergic reaction to tree nuts. These tests, such as the ImmunoCAP test, provide quantitative data on the severity of the allergy.
The qualitative data from a blood test just measures the presence of the antibodies reacting to allergens and is considered less accurate when compared to other diagnostic methods.
Oral Food Challenge
An oral food challenge is considered the gold standard for diagnosing food allergies. Under medical supervision, individuals consume increasing amounts of the suspected allergen while being monitored for any adverse reactions.
This method provides definitive confirmation of an allergy and helps determine the threshold dose that triggers symptoms.
In the case of tree nuts, you would be given small amounts of each type of tree nut and see if you have any reactions or symptoms immediately after consumption.
Tree Nut Allergy Treatment and Prevention Options
Living with a tree nut allergy requires vigilance and preparedness to manage potential allergic reactions effectively. While strict avoidance of tree nuts is the primary preventive measure, individuals with tree nut allergies should also be aware of the various treatment options available to address allergic reactions if they occur.
Epinephrine Auto-Injectors

Epinephrine auto-injectors (Epi-Pen®) are essential tools for individuals with severe tree nut allergies. These devices contain a single dose of epinephrine, a life-saving medication that can rapidly reverse the symptoms of anaphylaxis, a severe allergic reaction.
In the event of accidental ingestion or exposure to tree nuts, immediate administration of epinephrine can stabilize the individual’s condition and buy crucial time until emergency medical assistance arrives.
If you are new to Epi-pens, your doctor should give you training on how to administer. Additionally, most prescribed auto-injectors come with a training Epi-Pen (no needle or medication) so you can practice.
Antihistamines

Antihistamines are medications commonly used to alleviate mild allergic symptoms caused by tree nut exposure. By blocking the effects of histamine, a chemical released by the body during an allergic reaction, antihistamines can help reduce itching, hives, and other mild symptoms.
While antihistamines are not a substitute for epinephrine in cases of severe allergic reactions, they can provide relief for less severe symptoms, or daily allergy management.
Certain over-the-counter allergy medications are considered the best antihistamines for food allergies. Ensure you do your research and discuss these options with your provider.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy, specifically oral immunotherapy (OIT), is an emerging treatment option for individuals with severe tree nut allergies. This approach involves gradually exposing the individual to increasing amounts of the allergen under medical supervision, to desensitize the immune system over time.
While still considered experimental and not widely available, ongoing research into immunotherapy holds promise for offering long-term tolerance to tree nuts in some individuals.
Avoidance Strategies

Preventing exposure to tree nuts is the cornerstone of managing tree nut allergies. Avoidance strategies include carefully reading food labels to identify potential allergens, asking about ingredients when dining out or attending social events, and communicating allergy concerns to friends, family, and caregivers.
Additionally, individuals with tree nut allergies should be cautious of cross-contamination, as even trace amounts of tree nuts can trigger an allergic reaction.
Emergency Preparedness

In addition to carrying epinephrine auto-injectors, individuals with tree nut allergies should develop and maintain an emergency action plan in consultation with their healthcare provider. This plan should outline steps to take in the event of an allergic reaction, including administering epinephrine, seeking medical assistance, and monitoring symptoms.
Sharing this plan with family members, coworkers, and school personnel can ensure a prompt and coordinated response in case of an emergency.

It may also be important to wear an allergy emergency bracelet if you suffer from severe tree nut allergies.
The Future of Tree Nut Allergies

The future of tree nut allergies is likely to see advancements in several areas, especially with the currently ongoing studies. Here is a list of possible tree nut allergy advancements:
- Biotechnological Solutions: Advancements in biotechnology might lead to the development of hypoallergenic varieties of tree nuts, making them safer for consumption by individuals with allergies.
- Education and Awareness: Continued efforts to educate the public about tree nut allergies and how to prevent and manage allergic reactions are crucial. This includes raising awareness in schools, restaurants, and food manufacturing industries to minimize the risk of accidental exposure.
- Gene Therapy: Research into gene editing and gene therapy could potentially offer long-term solutions for tree nut allergies by targeting the underlying genetic factors that contribute to allergic reactions.
- Improved Diagnostic Tools: More accurate and efficient diagnostic tests may be developed, allowing for earlier detection of tree nut allergies. This could include more precise blood tests or advanced imaging techniques.
- Personalized Treatment Options: Tailored treatment approaches, such as immunotherapy or desensitization protocols, may become more widespread. These treatments aim to build tolerance to tree nuts gradually, reducing the severity of allergic reactions.
- Regulatory Measures: Governments may implement stricter labeling laws and allergen control regulations to ensure that products containing tree nuts are properly labeled and cross-contamination risks are minimized.
- Research into Gut Health: Emerging research suggests a link between gut health and allergies. Future studies may explore how interventions targeting the gut microbiome could potentially prevent or alleviate tree nut allergies.
Overall, while tree nut allergies present significant challenges, ongoing research, and technological advancements offer hope for improved management and potentially even a cure in the future.
Conclusion

In conclusion, tree nut allergies can be a serious health concern. Despite the prevalence of these allergies, there is still much we can do to raise awareness, provide support, and advocate for better research and treatment options.
Those with tree nut allergies must remain vigilant about reading labels, communicating their allergies to others, and seeking medical attention in case of accidental exposure.
Please read about specific tree nut allergies, share this post, and educate others!
